Being a FB white hat hacker, I get following questions frequently from people:
- Can you refer any reliable Facebook hacker? (After me denying their hacking request 😛 )
- Is there any online FB cracker tool?
- Where can I get FB hacking software?
- Is there any free password finder?
- How can I hack someone's Facebook account easily?
To the best of my knowledge, there is no hacking tool. You won't be able to find it anywhere. However, you will find many websites claiming that they are providing free hack tool (either online or offline), but you cannot download the password file without completing a survey. Even after going through a tiresome process of completing a survey, you would have got nothing in the end. These things are posted only with the intention of making money. Don't waste your precious time in searching such hack tool.
If you want to know how hackers can hack someone's FB account, please go ahead and read the techniques listed below. The most successful method among all of these techniques is phishing. Phishing enables someone with no or little technical knowledge to hack account's password easily in just a few minutes.
Some of the techniques listed below are not applicable only to FB but also to all daily used internet websites, such as Google, Twitter, Yahoo etc.
You won't be vulnerable to hacking if you understand how hacking works
This article is written with the aim of educating people about how hacking works and how should they prevent it. Please don't use these techniques for malicious purposes.
1 Phishing
Phishing is the most common technique used for hacking FB passwords. It is very easy for someone who is having little technical knowledge to get a phishing page done. That is why phishing is so popular. Many people have become a victim of Phishing page due to its trustworthy layout and appearance.
How does phishing work?
In simple words, phishing is a process of creating a duplicate copy of the reputed website's page with the intention of stealing user's password, or other sensitive information like credit card details. In our topic, it means creating a page which perfectly looks like FB login page but in a different URL like fakebook.com, or faecbook.com, or any URL that pretends to be legit. When a user lands on such a page, he/she may think that is the real Facebook login page, asking him/her to provide his/her username and password. So, the people who do not find phishing page suspicious are going to enter their username & password. The password information will be sent to the hacker who created the phishing page. At the same time, the victim gets redirected to original FB page.
Example: John is a programmer. He creates an FB login page with some scripts that enable him to get the username and password information. John puts this fake login page in https://www.facebouk.com/make-money-online-tricks. Peter is a friend of John. John sends a message to Peter, "Hey Peter, I have found a free trick to make money online, you should definitely take a look at https://www.facebouk.com/make-money-online-tricks-free". Peter navigates to the link and see a FB login page. As usual, Peter enters his username and password on it.
The hacking part
The username and password of Peter is sent to John and Peter is redirected to a money making tips page https://www.facebouk.com/make-money-online-tricks-tips-free.html. That's all; Peter's Facebook account is hacked.
Please note that phishing is done by a third person through emails; that is how it happens most of the time. So always beware of phishing emails, else you may lose your Facebook account, or credit card details, or any other sensitive data. Learn more about phishing.
How can you protect yourself against online FB phishing?
Hackers can reach you in many ways; email, personal messages, FB messages, website ads etc. Clicking any links from these messages will lead you to a FB login page. Whenever you find an FB login page, you should note only one thing which is URL. Because nobody can spoof/use Facebook URL except when there are some XSS zero-day vulnerabilities, but that's very rare.
- What is the URL you see in browser address bar?
- Is that really https://www.facebook.com/ (Trailing slash is very important since it is the only separator in Google chrome to distinguish domain and subdomain. Check out the below examples to know the difference)?
- Is there a green color secure symbol (HTTPS) provided in the address bar?
Bearing these questions in mind should prevent you from the hacking of online phishing pages. Also, see the below examples of phishing pages.
Some super perfect phishing pages
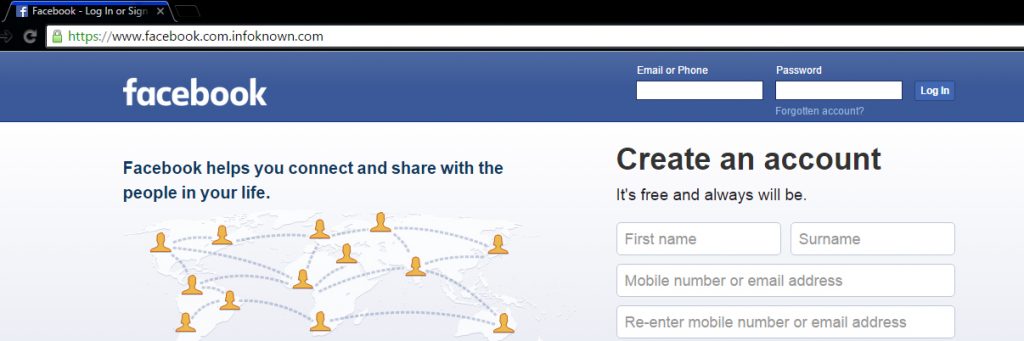
Most of the people won't suspect this page (snapshot given above) since there is an https prefix with a green color secure icon and also there is no mistake in www.facebook.com. But, this is a phishing page. How? Note the URL correctly. It is https://www.facebook.com.infoknown.com. So, www.facebook.com is a sub-domain of infoknown.com. Google Chrome does not differentiate the sub-domain and domain, unlike Firefox does.
One can obtain SSL Certificates (HTTPS) from many online vendors. A few vendors give SSL Certificate for Free for 1 year. It is not a big deal for a novice to create a perfect phishing page like the one given above. So, beware of it.
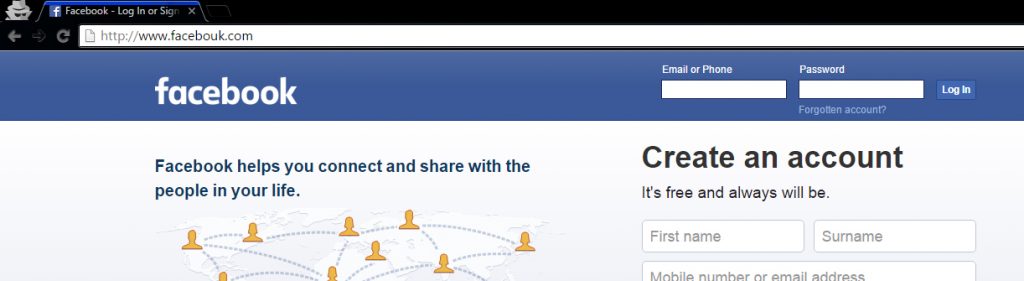
This is a normal FB Phishing page with some modification in the word Facebook.
2 Social Engineering
This is the second most common technique for hacking Facebook accounts. In fact, this method shouldn't come under Hacking, since much knowledge is not required for this method. I am listing this method under hacking to ensure the list of most common techniques used for FB account hacking in their respective order. Social engineering is basically a process of gathering information about someone, whose account you need to hack. The information may be his/her date of birth, mobile number, boyfriend/girlfriend's mobile number, nickname, mother's name, native place etc.
How does Social Engineering work?
Security Question
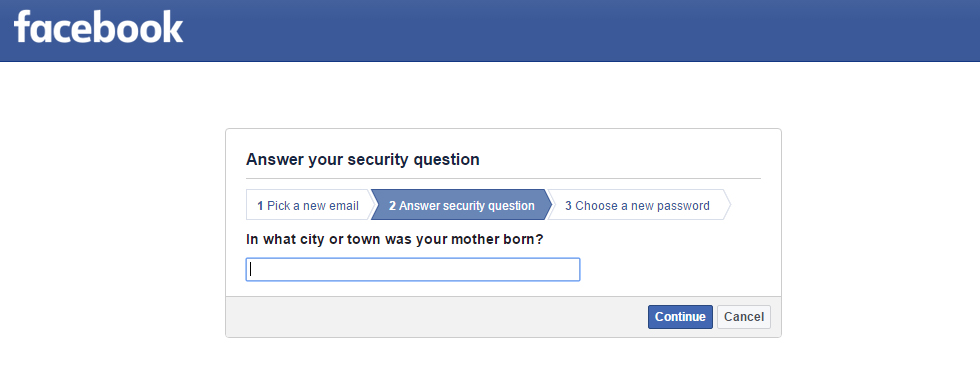
Many websites have a common password reset option called Security Question. Most common security questions are :
What is your nickname?
Who is your first-grade teacher?
What is your native place?
or
Any custom questions defined by the user.
Obtaining such information from the respective people may let us hack into their account. So, if anyone comes to know the answer to it, they will be able to hack your account using forgot password option.
Most Common and Weak Passwords
Security Question does not let you get into others FB account easily. But, setting a weak password could easily allow any of your friends to hack your account.
What is a weak password?
A password that is easily guessable by a third person is known as a weak password.
Most common passwords
- Mobile Number
- Nickname / Name and Date of Birth Conjunction
- Boy Friend's Mobile Number / Girl Friend's Mobile Number – Most of the lovers 😛
- Girl Friend's / Boy Friend's Name – Most of the lovers 😛
- Boy or Girl Friend Name Combination
- Bike Number
- Unused / Old Mobile Number
- Pet Name
- Closest Person Name (can be friends too)
Now, be honest and comment here if you are one of the people who have any one of the common passwords mentioned above. Please don't forget to change your password before making a comment 😉
How can you protect yourself from Social Engineering?
Security Question
Don't have a weak or familiar security question/answer. Therefore, it should be known only to you. You can set your security question here. Fortunately, Facebook has a lockout period of 24 hours before giving access to the one who successfully answered the security question, meaning that the hacker cannot enter into your account until 24 hours. So you can prevent the hacking attempt by logging in to your account in the 24 hours lockout period.
Additionally, FB provides an option called "Login Alerts" under Facebook Security Settings. You should add your mobile or email there to get notified whenever your account is logged in to a new or unknown device.
Most Common and Weak Passwords
It is very simple. Change your password now if you have any one of the weak passwords stated above.
You might also be interested in hacking facebook fan page article
3 Plain Password Grabbing

This is another common method used to steal Facebook user's password. Most people are unaware of this method, but traditional hackers use this method to hack user accounts.
How does Plain Password Grabbing works?
In this method, the Facebook hacker targets a particularly low-quality website, where the victim is a member and hacks their database to get the stored plain username & password of victim.
How could the hacker/attacker get access to Facebook?
Many of us use the same password for FB and also for some poor xyz.com. So, it is easy for a hacker to get your password through the low-quality poorxyz.com.
In another scenario, the hacker/attacker creates a website with the intention of getting victim's password, so when the victim registers his/her account using email and creates a password, those details will get stored in the database of the hacker/attacker. Thus hacker gets access to victim's account.
Common people, who use same email and password for these kinds of low-quality websites, may end up losing their Facebook account.
How can you protect yourself from Facebook Plain Password Grabbing?
You should never trust the third party low-quality websites. Even passwords of popular websites, like LinkedIn, are insecure and vulnerable to hacking. So, never and ever trust the third party low-quality websites.
Most of the website developers are storing plain passwords in their database without even thinking about encryption or security. This makes Facebook hackers' job easy since the password is in plain text format.
Best way to prevent this method is to have a unique password at least for websites that you really trust. Don't use your FB password for any other website/portal, so your password will be safe .
4 Key Logger

A keylogger is a software tool used to record keystrokes on a computer or mobile device. This, in turn, records everything you type using your keyboard and store it for use. Generally, keyloggers are installed as application software in operating systems to track keystrokes, but there are hardware keyloggers as well.
Hardware keyloggers also are known as physical keyloggers attached to a computer in a USB port records everything before it sends the keyboard data to the computer. There are various mobile keyloggers, that perform the same action on various operating systems.
How Key Logging works?
All keyloggers run in the background (except trial versions) and won't be viewable to users until you know the keylogger password and shortcut used to view it. It will record all the keys pressed and give you a detailed report of when and what keys are used for what application – Simply, a clean report to identify passwords.
Anyone who is reading the keylogger logs is able to see the Facebook password or any passwords and sensitive information typed, like credit cards, bank username, password etc. Whenever you log in to a public computer, there are chances to lose your Facebook password to someone else.
Hardware keyloggers are identifiable in case of your personal computer but are hard in case of public computers.
In another scenario, your friend/colleague/neighbor could ask you to log in using their computer as a help. If their intention is to get your password, then you are most likely to lose your Facebook account to the hacker.
Nowadays, many people are using mobile keyloggers. It enables to track the keypad of mobile. So, any sensitive information typed on the mobile keypad is vulnerable to hacking.
How can you protect yourself from Key Logging?
You need not be afraid of keyloggers when you use your personal computer since you are the only one who is going to access it. But, whenever you use any public computer or your friend's computer, you should not trust it.
I always suggest my friends use On-Screen Keyboard whenever they are in need to type a password. Also, please make sure that nobody is checking your screen when you type your password because your screen would expose what you had typed. In windows, there is an inbuilt tool called On-Screen Keyboard that helps us to select keys using the mouse.
You can open OSK by using the Run dialog box. Winkey + R to open Run dialog box, type OSK and then press Enter. Nowadays, many banking portals provide a screen keyboard in the browser itself. So, please make use of it whenever you are surfing on public computers. On-Screen Keyboard helps even when hardware keyloggers are installed.
Never use third-party mobile keypad apps unless you really trust the publisher because the app may track all of your keystrokes and send it to the publisher.
5 Browser Extension Hacker
This method doesn't let the Facebook hacker/attacker gain complete access to your Facebook account, however, gives some power to control your account indirectly. I've seen multiple Google Chrome and Firefox add-ons, which secretly perform actions, like following a person, like a page on behalf of your Facebook profile, etc.
How Browser extension hack works?
When you visit some malicious websites or web pages, you will be prompted to install a browser add-on. Once you install the add-on, it will perform all the tasks described by the hacker or attacker who created it. Some primary actions are posting status updates on your wall, liking an FB page, following a person, adding you to some Facebook groups, inviting your friends to like a page, or join a Facebook group etc. You may not know these things happening on your FB account until you check your Facebook activity log periodically.
How can you prevent browser extension Facebook hack?
You should monitor your activities using Activity Log. You must not trust any third party websites prompting you to add a browser extension. Install add-on only from the browser store, that too only from trusted publishers. Why should you risk your account if you don't know the publisher or intention of the add-on? Therefore, always stay away from these malicious browser extensions.
6 Malicious Application Hack
Always remember that all the apps you use on Facebook are owned by third-party publishers and not by Facebook. Of course, there are a few exceptions like Instagram. A malicious application, which is requesting your permission, will do almost all kind of spam stuff on your Facebook profile.
How malicious application hack works?
Whenever you find Login using the Facebook option on any website, you should come to know that it is a third party Facebook application not owned by Facebook. When you click Login using Facebook, you will be shown a permission dialog box with the requested permission details. Once you click okay button, the requested personal details can be accessed from FB or the requested actions can be performed in your FB account on your behalf.
What could a third party application do on your Facebook account?
- Post photos and status update
- Share link to your timeline or to any group you belong
- Manage your page
- Post on behalf of you on the Facebook pages you own
- Access your personal information
- Access your photos including "Only me" privacy photos; sometimes they can further access your mobile photos using a Facebook vulnerability like the one I found (Don't worry, it's completely fixed now 😉 ).
These are just examples of what can be done. What if the application you are using is malicious? It could spam your Facebook account with a bunch of worthless contents.
How can you prevent yourself from malicious application hack?
You should always beware of what permissions you give to a Facebook application even though FB is reviewing application's permission requests. Don't give permission to an application if you don't trust the website or application.
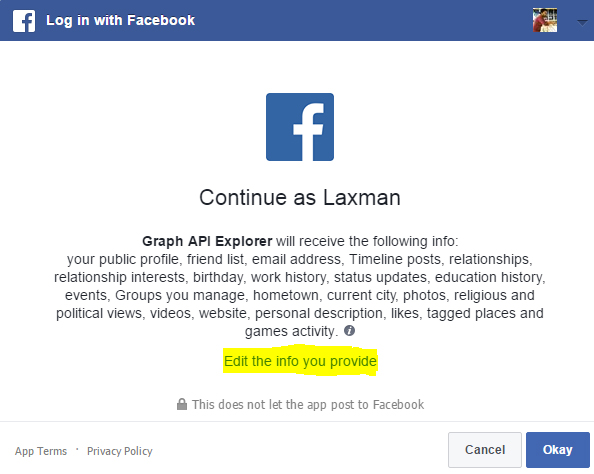
You can edit the information that you give to an application in the permission dialog box (snapshot given above). Also, you should review the applications that have access to your Facebook account here if you think you had given access to malicious applications.
7 Facebook Account Hacker Software
You might have seen or downloaded many Facebook account hacker software, but none of them could truly hack Facebook password. Hacking your Facebook password instead of the target user is what it actually does.
How does Facebook account hacker software work?
People who try to hack Facebook account usually download software that is available on various websites. The software will collect the victim's password (the one who downloaded this software) as soon as it is opened or installed. Some software prompt you to enter Facebook username and password. They will store your password in their database collection of passwords. Few other software gain administrative privilege from you to install background keylogger to get your keystrokes including the Facebook password.
How can you prevent yourself from Facebook hacking software?
Don't trust Facebook hacking software. There is no real hacking software available on the Internet as I had said earlier.
8 Malicious Mobile Application
There are a lot of mobile applications that secretly steal Facebook access token from your mobile device. Facebook mobile app functions through API, where access-token stored in your mobile's internal memory is used for authentication. It is more like your username and password. So, if someone steals your access-token, then he/she is likely to have full access to your Facebook account.
How malicious mobile application software works?
Facebook Application Interface do not require username or password every time to get user data. It just needs secret access-token to retrieve user's data. Facebook mobile app stores the access token in mobile's memory. The app's part of the memory is accessible only to the respective application. Mobile apps that have administrative privilege can access other app's data. For example, gaining admin privilege in a rooted android phone could allow an application to steal your access token. A hacker can do a lot of malicious things if he/she gets your access token.
How can you prevent yourself from malicious mobile applications?
- Install mobile apps only from trusted publishers.
- Don't root your mobile device.
- Logout Facebook from your mobile device frequently to get your access token expired.
- Change your Facebook password frequently.
9 Browser Vulnerabilities

Browser Vulnerabilities are security bugs, which exist in older versions of mobile and desktop browsers.
How does browser vulnerabilities work on Facebook hacking?
Most browser vulnerabilities are exploited through an older version of the browser since all the zero days are patched by browser vendor once it is reported by researchers around the world. For example, Browser Same Origin Policy Vulnerability could allow a hacker/attacker to read the response of any Page like facebook.com and could be able to perform any action on your Facebook account since they are able to read the response by accessing the Facebook origin. Android Chrome SOP bypass by Rafay Baloch is one such vulnerability that is affecting Android web-view in Android < 4.4.
How can you prevent yourself from browser vulnerabilities?
You should always update your browser and operating system once there is an update available. Keeping an older version always has many risk factors involved.
Self XSS is also known as Self Cross Site Scripting. XSS is basically a web security vulnerability, which enables hackers to inject scripts into web pages used by other users. What is self XSS then? Self XSS is a kind of social engineering attack, where a victim accidentally executes a script, thus exploiting it to the hacker.
How does self XSS scam work?
In this method, hacker promises to help you hack somebody else's FB account. Instead of giving you access to someone else's account, the hacker tricks you into running malicious Javascript in your browser console that gives a hacker the ability to manipulate your account. Facebook hackers use this technique to add you in groups, add your friends to the group, post on your wall, add your friends in comments etc.
How can you prevent yourself from self XSS?
Self XSS is something that you let hackers to hack your account. So never and ever copy & paste the code given by someone in your browser, otherwise, you will get your Facebook account hacked.
11 Trojan Horses
Trojan Horse is a malicious program, which is used to spy and control a computer by misleading users of its true intent. Malware Trojan can also be called as Remote Key Logger since it records keystrokes of all the applications of our computer and sends it to the hacker online.
How do Trojan Horses work?
A software you think legit might be a trojan. A PDF you don't suspect might contain a trojan. An AVI media file given by someone might be a trojan. The Trojan horse runs in the background process, collects information and send it to the hacker. Trojan Horse can be sent in any form through any medium, like pen drive, iPod, website, or email. In our topic, Trojan records FB password that you have typed in your browser and sends it to the Facebook hacker using the Internet.
How can you prevent yourself from Trojan?
- Do not
- install programs from unknown online sources
- play media files received from an unknown source
- open any kind of files downloaded from untrusted sources
- insert pen drive from any suspicious people.
- Do have an updated anti-virus software installed on your computer.
Keeping your anti-virus software up to date does not guarantee you to stay safe from hacking. Basically, an anti-virus software is a collection of detected malware and viruses. Its job is to compare each and every file with the database of viruses. There are many numbers of software, which enable us to create undetectable Trojans. But, it is very unlikely to target a common man with undetectable Trojanware. So, keeping an antivirus program up to date is protective to large extent. Don't forget to update your anti-virus software once an update is available.
12 FB Zero Day
Zero Day is a security vulnerability that is unknown to the respective software vendor. In our context, undiscovered Facebook vulnerabilities are called FB Zero Day.
How does Zero Day hacking work?
FB Zero Day vulnerabilities are very rare since Facebook has a bug bounty program, where security researchers around the world participate and report zero-day vulnerabilities. Zero-day is basically a security loophole that is unknown to the software vendor.
There are two types of people who find Zero Day vulnerabilities. The first case is Security Researchers and Bug hunters, who make a responsible disclosure about the vulnerability to the software vendor; FB in our context. Another case falls on the evil side. Blackhat hackers who find Zero Day vulnerabilities don't disclose it to Facebook and they will use it for their personal benefit of hacking.
@EVERYTHING NT















